Comments from Expert Advisory Group
Tinea capitis is more common in children (under 12 years) than adults and requires an urgent dermatology referral.
In the presence of a kerion or where one or more of the cardinal clinical signs is present (scale, lymphadenopathy, alopecia) it is reasonable to commence treatment while awaiting confirmatory mycology and/or dermatology opinion. Mycology results take at least two weeks to process.
Treatment should be prompt to avoid scarring alopecia.
Suspected tinea capitis lesions should be sampled either by plucking hairs, using a blunt scalpel to remove hair and scalp scale, or by taking scalp brushings. Samples should be sent for microscopy and culture.
Skin sampling instruction
- Swabs are of little value for dermatophytes, unless there is insufficient material obtained by scraping
- Wipe off any treatment creams before sampling
- Keep any samples at room temperature. Do not refrigerate as dermatophytes are inhibited at low temperatures, and humidity facilitates the growth of contaminants
- Samples should be collected into folded dark paper squares. Secure dark paper squares with a paper clip and place in a plastic bag, or use commercially available fungal packets
Hair samples
- take scalp scrapings, as this often pulls out infected hair stumps, which are critical for successful culture and microscopy; hair plucking does not produce the best samples
- a soft toothbrush can be used if scrapings are not possible
Skin scrapings
- Scrape skin from the advancing edge of lesion; use a blunt scalpel blade or similar
- 5mm2 of skin flakes are needed for microscopy and culture
General advice
- Screen all family members
- Treat household with ketoconazole shampoo to prevent re-infection
- Children on appropriate therapy should not be excluded from school
- Disinfect hair brushes, combs, razors. Do not share brushes to prevent spread
Consider 2nd line agent in case of treatment failure.
|
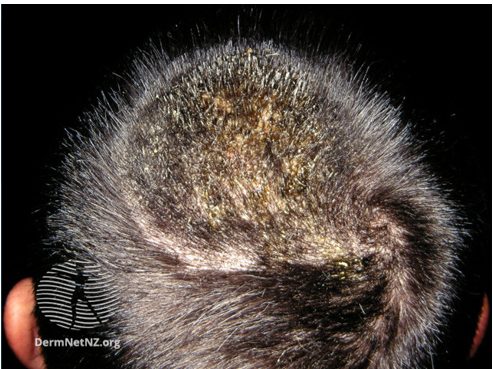
Image 1: Kerion
Image source/Credit: Dermnet
|
 |
|
Image 2: Tinea capitis – Alopecia
Image source/Credit: Dermnet
|
 |
|
Image 3: Black dot scalp ringworm
Image source/Credit: Dermnet
|
 |
|
Image 4: Scale, pustules and patchy hair loss in tinea capitis
Image source/Credit: Dermnet
|
 |
Treatment
| Tinea capitis: Children |
| Drug |
Dose |
Duration |
Notes |
| 1st choice options (Children) |
|
Griseofulvin**
|
10mg/kg every 24 hours
|
6-8 weeks
|
Take with a fatty meal to increase absorption.
Only licensed form is a 500mg film coated tablet therefore only suitable for children who can swallow, and >50kg.
Not recommended in patients with active or chronic liver disease.
Use with caution in cases of a history of penicillin allergy.
Griseofulvin is contraindicated in pregnancy**.
Supply issues may preclude the use of griseofulvin in the community. Please contact your community pharmacist prior to prescribing.
|
|
OR
Itraconazole* (unlicensed in children)
|
Child 1–17 years
3–5 mg/kg every 24 hours (max. per dose 200 mg)
|
2–6 weeks
|
Unlicensed indication.
Take capsules immediately after a meal for maximum absorption.
Oral solution should be taken on an empty stomach, at least one hour before food.
Not recommended in patients with active or chronic liver disease.
If treatment is for longer than one month then pre-treatment LFTs should be performed and then monitored.
Avoid itraconazole (and all oral azoles) in pregnancy*.
|
|
OR
Terbinafine
(unlicensed in children)
|
20-40kg: 125mg (half of 250mg tablet) every 24 hours
>40kg: 250mg (one 250mg tablet) every 24 hours |
2-4 weeks
|
Not recommended in patients with active or chronic liver disease.
Pre-treatment LFTs should be performed. If treatment is to continue beyond 4 weeks then repeat LFTs should be performed.
|
| Tinea capitis: Adults |
| Drug |
Dose |
Duration |
Notes |
| 1st choice options (Adults) |
|
Terbinafine
|
250mg every 24 hours
|
4 weeks
|
Unlicensed indication.
Not recommended in patients with active or chronic liver disease.
Pre-treatment LFTs should be completed. If treatment is to continue beyond 4 weeks then repeat LFTs should be completed.
|
|
OR
Itraconazole*
|
5 mg/kg every 24 hours (maximum 400 mg per day)
|
4 weeks
|
Unlicensed indication.
Not recommended in patients with active or chronic liver disease.
Avoid itraconazole (and all oral azoles) in pregnancy*.
Take capsules immediately after a meal for maximum absorption.
|
| * Women of childbearing potential taking itraconazole should use contraceptive precautions. Effective contraception should be continued until the menstrual period following the end of itraconazole therapy |
| 2nd choice Option (Adults) |
|
Griseofulvin**
|
500mg every 12 hours
OR
1000mg every 24 hours
NB: Dose no less than 10mg/kg every 24 hours
|
6-8 weeks
|
Take with a fatty meal to increase absorption.
Not recommended in patients with active or chronic liver disease.
Use with caution in cases of a history of penicillin allergy.
Griseofulvin is contraindicated in pregnancy**.
Supply issues may preclude the use of griseofulvin in the community. Please contact your community pharmacist prior to prescribing.
|
| ** Women of childbearing potential have to use effective contraception during (and up to 4 weeks after) treatment. In respect of effect on oral contraceptives, and contraceptive precautions: efficacy of oral contraception is reduced during griseofulvin therapy and for four weeks post therapy cessation. In view of the contraindication in pregnancy and of the possible sequelae of male patients fathering a child during therapy, all sexually active patients should use additional barrier contraception, such as condoms, throughout griseofulvin therapy, and for four weeks (female) and 6 months (male) post therapy cessation. |
Patient Information
Reviewed December 2022
